Top
PLPP6
| Gene Name | PLPP6 (QuickGO) | (A quick tutorial to explore the interctive visulaization) |
| Synonyms | PLPP6 , PPAPDC2 | |
| Protein Name | PLPP6 |
|
| Alternative Name(s) |
Phospholipid phosphatase 6;3.1.3.-;Phosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2 domain-containing protein 2;PPAP2 domain-containing protein 2;Presqualene diphosphate phosphatase; | |
| EntrezGene ID | 403313 (Comparitive Toxicogenomics) | |
| UniProt AC (Human) | Q8IY26 (protein sequence) | |
| Enzyme Class | N/A | |
| Molecular Weight | 32194 Dalton | |
| Protein Length | 295 amino acids (AA) | |
| Genome Browsers | NCBI | ENSG00000205808 (Ensembl) | UCSC | |
| Crosslinking annotations | Query our ID-mapping table | |
| Orthologues | Quest For Orthologues (QFO) | GeneTree | |
| Classification | Superfamily: glucose_lipid phosphatases | Historic class: Phosphatidic acid phosphatase (PAP) | CATH ID: 1.20.144.10 | SCOP Fold: Chloroperoxidase | |
| Phosphatase activity | active | Catalytic signature motif: unknown | |
| Phosphorylation Network | Visualize | |
| Domain organization, Expression, Diseases | (show / hide) |
| Protein Domain | InterPro | Pfam | SMART | 3D Structure | PDB | DrugPort | ModBase | SwissModel |
| Polypeptide organization (Pfam) | No Pfam domain found | ||
| Catalytic Site | Mechanism and Catalytic Site Atlas | ||
| Gene Expression | Gene Expression Atlas | Diseases | OMIM | ClinVar |
| Protein-protein interactions | STRING | IntAct | MINT | BioGRID | ||
| Phosphosites | Phospho.ELM | PhosphoSitePlus | ||
| Localization, Function, Catalytic activity and Sequence | (show / hide) |
| Localization (UniProt annotation) | |||
| Membrane | |||
| Function (UniProt annotation) | |||
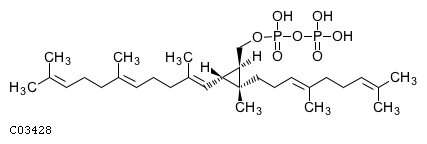
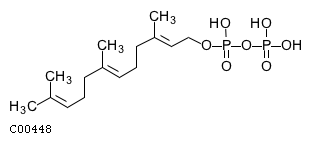
| Phosphatase that dephosphorylates presqualenediphosphate (PSDP) into presqualene monophosphate (PSMP),suggesting that it may be indirectly involved in innate immunityPSDP is a bioactive lipid that rapidly remodels to presqualenemonophosphate PSMP upon cell activation Displays diphosphatephosphatase activity with a substrate preference for PSDP > FDP >phosphatidic acid | |||
| Catalytic Activity (UniProt annotation) | |||
| NA | |||
| Protein Sequence | |||
| MPSPRRSMEGRPLGVSASSSSSSPGSPAHGGGGGGSRFEFQSLLSSRATAVDPTCARLRASESPVHRRGSFPLAAAGPSQ SPAPPLPEEDRMDLNPSFLGIALRSLLAIDLWLSKKLGVCAGESSSWGSVRPLMKLLEISGHGIPWLLGTLYCLCRSDSW AGREVLMNLLFALLLDLLLVALIKGLVRRRRPAHNQMDMFVTLSVDKYSFPSGHATRAALMSRFILNHLVLAIPLRVLVV LWAFVLGLSRVMLGRHNVTDVAFGFFLGYMQYSIVDYCWLSPHNAPVLFLLWSQR |
| Motif information from Eukaryotic Linear Motif atlas (ELM) | (show / hide) |
| Gene Ontology (P: Process; F: Function and C: Component terms) | (show / hide) | |
| GO:0005886 | C:plasma membrane |
| GO:0006695 | P:cholesterol biosynthetic process |
| GO:0016021 | C:integral component of membrane |
| GO:0016787 | F:hydrolase activity |
| GO:0042577 | F:lipid phosphatase activity |
| GO:0046839 | P:phospholipid dephosphorylation |