
CHEBI:18132
| Name | phosphocholine | 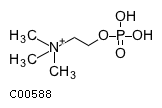 Download: mol | sdf |
| Synonyms | 02-(trimethylazaniumyl)ethyl phosphate; Choline phosphate; Chop; O-phosphocholine; Pcho; Phosphocholine; Phosphorylcholine; Trimethyl(2-(phosphonooxy)ethyl)ammonium; | |
| Definition | The phosphate of choline; and the parent compound of the phosphocholine family. | |
| Molecular Weight (Exact mass) | 184.1507 (184.0739) | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H15NO4P | |
| SMILES | C[N+](C)(C)CCOP(O)(O)=O | |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C5H14NO4P/c1-6(2,3)4-5-10-11(7,8)9/h4-5H2,1-3H3,(H-,7,8,9)/p+1 | |
| InChI Key | YHHSONZFOIEMCP-UHFFFAOYSA-O | |
| Crosslinking annotations | KEGG:C00588 | 3DMET:B00141 | CAS:107-73-3 | ChEBI:18132 | ChEMBL:CHEMBL1235161 | ChEMBL:CHEMBL3350840 | KNApSAcK:C00007299 | NIKKAJI:J215.288F | PDB-CCD:PC | PubChem:3867 | |
| Pathway ID | Pathway Name | Pathway Description (KEGG) |
| map00564 | Glycerophospholipid metabolism | NA |
| map01100 | Metabolic pathways | NA |
| map05231 | Choline metabolism in cancer | Abnormal choline metabolism is emerging as a metabolic hallmark that is associated with oncogenesis and tumour progression. Following transformation, oncogenic signalling via pathways such as the RAS and PI3K-AKT pathways, and transcription factors associated with oncogenesis such as hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF1) mediate overexpression and activation of choline cycle enzymes, which causes increased levels of choline-containing precursors and breakdown products of membrane phospholipids. These products of choline phospholipid metabolism, such as phosphocholine (PCho), diacylglycerol (DAG) and phosphatidic acid, may function as second messengers that are essential for the mitogenic activity of growth factors, particularly in the activation of the ras-raf-1-MAPK cascade and protein kinase C pathway. |

