Top
PLPPR4
| Gene Name | PLPPR4 (QuickGO) | (A quick tutorial to explore the interctive visulaization) |
| Synonyms | PLPPR4 , KIAA0455 | |
| Protein Name | PLPPR4 |
|
| Alternative Name(s) |
Phospholipid phosphatase-related protein type 4;3.1.3.4;Brain-specific phosphatidic acid phosphatase-like protein 1;Lipid phosphate phosphatase-related protein type 4;Plasticity-related gene 1 protein;PRG-1; | |
| EntrezGene ID | 9890 (Comparitive Toxicogenomics) | |
| UniProt AC (Human) | Q7Z2D5 (protein sequence) | |
| Enzyme Class | EC 3.1.3.4 (BRENDA | |
| Molecular Weight | 82983 Dalton | |
| Protein Length | 763 amino acids (AA) | |
| Genome Browsers | NCBI | ENSG00000117600 (Ensembl) | UCSC | |
| Crosslinking annotations | Query our ID-mapping table | |
| Orthologues | Quest For Orthologues (QFO) | GeneTree | |
| Classification | Superfamily: glucose_lipid phosphatases | Historic class: Phosphatidic acid phosphatase (PAP) | CATH ID: 1.20.144.10 | SCOP Fold: Chloroperoxidase | |
| Phosphatase activity | active | Catalytic signature motif: unknown | |
| Domain organization, Expression, Diseases | (show / hide) |
| Protein Domain | InterPro | Pfam | SMART | 3D Structure | PDB | DrugPort | ModBase | SwissModel |
| Polypeptide organization (Pfam) | No Pfam domain found | ||
| Catalytic Site | Mechanism and Catalytic Site Atlas | ||
| Gene Expression | Gene Expression Atlas | Diseases | OMIM | ClinVar |
| Protein-protein interactions | STRING | IntAct | MINT | BioGRID | ||
| Phosphosites | Phospho.ELM | PhosphoSitePlus | ||
| Localization, Function, Catalytic activity and Sequence | (show / hide) |
| Localization (UniProt annotation) | |||
| Membrane | |||
| Function (UniProt annotation) | |||
| Hydrolyzes lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) Facilitatesaxonal outgrowth during development and regenerative sprouting Inthe outgrowing axons acts as an ecto-enzyme and attenuatesphospholipid-induced axon collapse in neurons and facilitatesoutgrowth in the hippocampus | |||
| Catalytic Activity (UniProt annotation) | |||
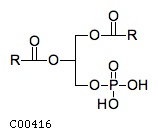
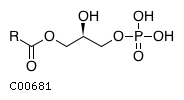
| A 1,2-diacylglycerol 3-phosphate + H(2)O = a1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol + phosphate | |||
| Protein Sequence | |||
| MQRAGSSGGRGECDISGAGRLGLEEAARLSCAVHTSPGGGRRPGQAAGMSAKERPKGKVIKDSVTLLPCFYFVELPILAS SVVSLYFLELTDVFKPVHSGFSCYDRSLSMPYIEPTQEAIPFLMLLSLAFAGPAITIMVGEGILYCCLSKRRNGVGLEPN INAGGCNFNSFLRRAVRFVGVHVFGLCSTALITDIIQLSTGYQAPYFLTVCKPNYTSLNVSCKENSYIVEDICSGSDLTV INSGRKSFPSQHATLAAFAAVYVSMYFNSTLTDSSKLLKPLLVFTFIICGIICGLTRITQYKNHPVDVYCGFLIGGGIAL YLGLYAVGNFLPSDESMFQHRDALRSLTDLNQDPNRLLSAKNGSSSDGIAHTEGILNRNHRDASSLTNLKRANADVEIIT PRSPMGKENMVTFSNTLPRANTPSVEDPVRRNASIHASMDSARSKQLLTQWKNKNESRKLSLQVIEPEPGQSPPRSIEMR SSSEPSRVGVNGDHHGPGNQYLKIQPGAVPGCNNSMPGGPRVSIQSRPGSSQLVHIPEETQENISTSPKSSSARAKWLKA AEKTVACNRSNSQPRIMQVIAMSKQQGVLQSSPKNTEGSTVSCTGSIRYKTLTDHEPSGIVRVEAHPENNRPIIQIPSTE GEGSGSWKWKAPEKGSLRQTYELNDLNRDSESCESLKDSFGSGDRKRSNIDSNEHHHHGITTIRVTPVEGSEIGSETLSI SSSRDSTLRRKGNIILIPERSNSPENTRNIFYKGTSPTRAYKD |
| Motif information from Eukaryotic Linear Motif atlas (ELM) | (show / hide) |
| Gene Ontology (P: Process; F: Function and C: Component terms) | (show / hide) | |
| GO:0005886 | C:plasma membrane |
| GO:0005887 | C:integral component of plasma membrane |
| GO:0006644 | P:phospholipid metabolic process |
| GO:0007165 | P:signal transduction |
| GO:0007409 | P:axonogenesis |
| GO:0008195 | F:phosphatidate phosphatase activity |
| GO:0042577 | F:lipid phosphatase activity |
| GO:0046839 | P:phospholipid dephosphorylation |
| GO:0048839 | P:inner ear development |
| GO:0098978 | C:glutamatergic synapse |
| GO:0099061 | C:integral component of postsynaptic density membrane |